AMERICAN BLACK WALNUTS:
THE WILD SUPERFOOD
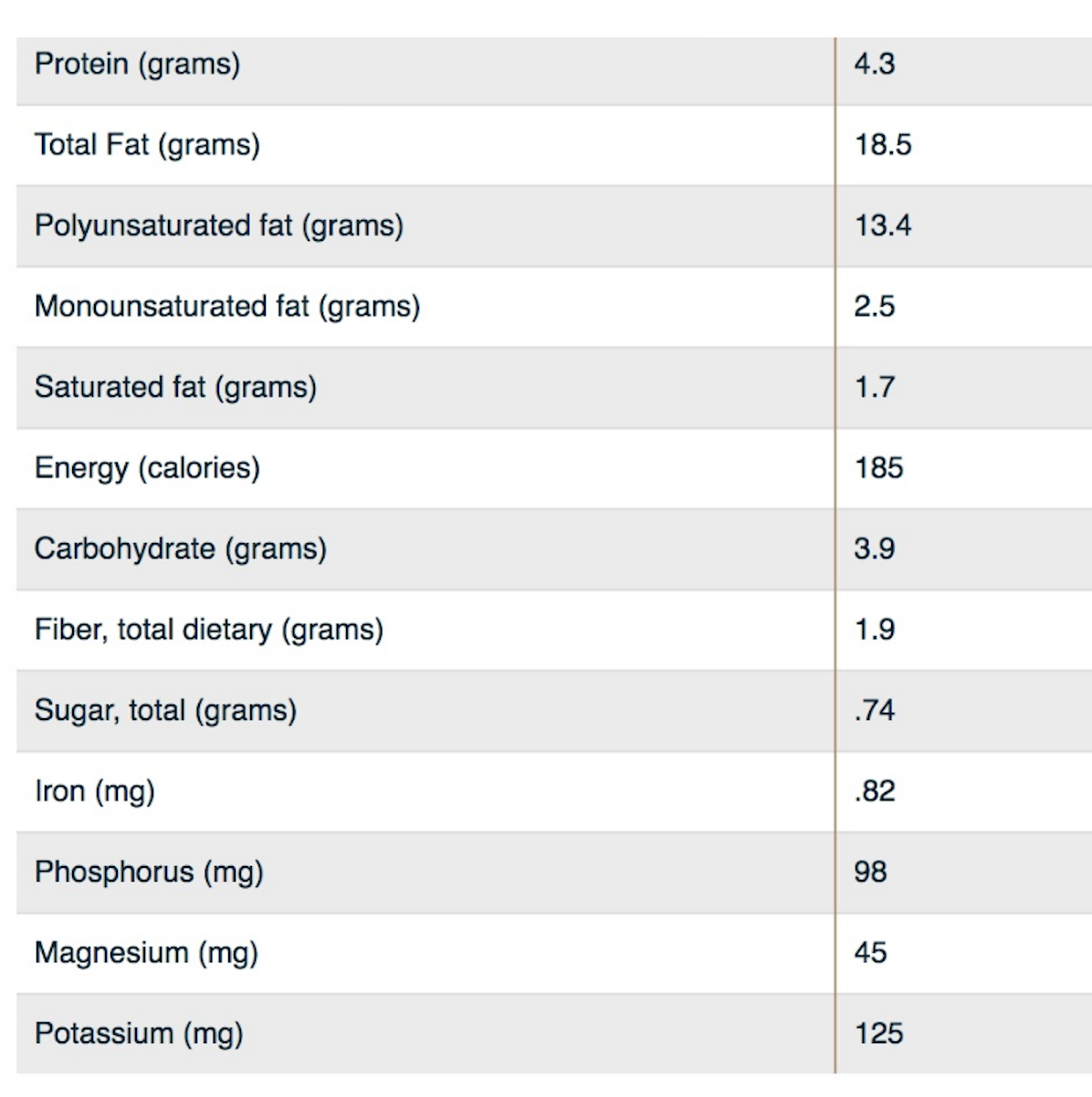
Nutrition Facts: Black Walnuts Vs. English Walnuts
The health benefits gained by adding Black Walnuts to your diet are extensive, according to numerous recent studies. Black Walnuts contain 57% more protein than English walnuts and have the highest levels of protein of all tree nuts. Compared with five other tree nuts, Black Walnuts contain the most protein and the fewest carbohydrates and starches. On the vitamin front, Black Walnuts contain the most panthothenic acid and the highest quantity of vitamin B-6. So not only do Black Walnuts add culinary zest to your favorite recipes, they support a healthy diet.
Black Walnuts
English Walnuts
(Amounts based on 1 ounce – 1/4 cup serving size)
USDA National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference, Release 16 (July 2003)
THE BENEFITS OF BLACK WALNUTS
Incredible health benefits are packed inside each Black Walnut nugget. With the highest protein of any tree nut, Black Walnuts are also low in saturated fat, high in unsaturated fat, contain vitamin A, iron, minerals and fiber. Black Walnuts are a highly nutritious, cholesterol- and sugar-free ingredient that can add tremendous appeal to a wide variety of food products.
Black Walnuts are delicious in dessert dishes and a health food powerhouse that can add a nutritional boost to your diet. Adding Black Walnuts to dishes like salads, yogurt and oatmeal, or by using Black Walnuts as an ingredient nut in fish or chicken recipes, brings added benefits and flavor to your everyday dishes.
Nutritional Studies
Frontier in Nutrition: Nutrition and Food Science Technology Article
Quantification of Vitamins, Minerals, and Amino Acids in Black Walnut (Juglans nigra)
Article aimed to quantify the micronutrients in black walnut and address its human health benefits.
Metabolites
Identifying Antibacterial Compounds in Black Walnuts (Juglans nigra) Using a Metabolomics Approach
Technical paper in which six antibacterial bioactive compounds responsible for antimicrobial activity were were evaluated for their antibacterial activities using agar-well diffusion assay. Published in “metabolites” by MDPI, Basel, Switzerland.
Journal of Food Composition and Analysis
Identification and Quantification of Phytosterols in Black Walnut Kernels
Technical study identifies and and quantifies phytosterols of six Black Walnut (Juglans nigra L.) varieties, and compares the levels of these phytosterols between Black Walnuts and English Walnuts. Published in the “Journal of Food Composition and Analysis” by Elsevier.
Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry
Identification and Characterization of Phenolic Compounds in Black Walnut Kernels
Technical study identifies and characterizes the phenolic contents of 11 different Black Walnut cultivars and compares the levels of these phenolics between Black Walnuts and English Walnut (Juglans regia L.). Published in the “Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry”
University of Nebraska Study
Black Walnuts (Juglans nigra L.): Potential as a Health Promoting Food
Evaluation of Black Walnut consumption on human-health promotion, using recent evidences obtained from English Walnuts research, as both classes have comparable bioactive compounds composition. Paper published by the Dept. of Food Science and Technology, Univ. of Nebraska.
Nutrition Research - University of Georgia
Acute Consumption of Black Walnuts Increases Fullness and Decreases Lipid Peroxidation in Humans (Abstract Version)
Abstract for a research study that indicates Walnut Walnuts contain a different antioxidant and fatty acid profile, and more protein, compared to English Walnuts. Paper published by Elsevier.